Hemophilia1 is an inherited bleeding disorder in which the blood does not clot properly. This can lead to spontaneous bleeding as well as bleeding following injuries or surgery. Jay Harold’s Post, “8 Signs and Symptoms of Hemophilia: Healthy Living Tips,” talks about this rare, costly and potentially fatal disease.
Blood contains many proteins called clotting factors that can help to stop bleeding. People with hemophilia have low levels of either factor VIII (8) or factor IX (9). The severity of hemophilia that a person has is determined by the amount of factor in the blood. The lower the amount of the factor, the more likely it is that bleeding will occur which can lead to serious health problems.
Hemophilia’s Effect on Russian History
The son of Tsar Nicholas II (Tsarevich Alexei Romanov) had hemophilia B according to an article in Science Magazine2. The disease impacted not only the Romanov family but also probably Russian history, says Evgeny Rogaev, a geneticist at the University of Massachusetts Medical School in Worcester. Alexei’s frail condition encouraged his mother Alexandra to keep close company with the Russian mystic Grigori Rasputin, who claimed to wield healing magic. “There was no medication at that time,” Rogaev says. “She tried to do everything possible.” According to some historians, when Rasputin used his close relationship with the Romanovs to influence bureaucratic affairs in his favor, the public grew increasingly suspicious of the regime, possibly hastening the revolution.
Bleeding Disorders Facts from The National Hemophilia Foundation3
- The worldwide incidence of hemophilia is not well known but estimated at more than 400,000 people. Approximately 75% of people with hemophilia around the world still receive inadequate treatment or have no access to treatment.
- There is currently no cure for hemophilia. There are very effective treatments available in the US, but they may require a lifelong infusion of expensive drugs that are manufactured from human plasma or through recombinant biotechnology.
- Nearly 90% of Americans with severe hemophilia became infected with AIDS in the 1980s when blood and plasma donations in the US were not properly screened for HIV.
- Improvements in donor screening and current viral inactivation measures in the commercial manufacturing process have made clotting factor products are very safe. CDC’s blood safety surveillance system, in place since 1998, has found no reported cases of HIV or hepatitis infections associated with clotting factor products among hemophilia patients.
Causes
Hemophilia is caused by a mutation or change, in one of the genes, that provides instructions for making the clotting factor proteins needed to form a blood clot. This change or mutation can prevent the clotting protein from working properly or to be missing altogether. These genes are located on the X chromosome. Males have one X, and one Y chromosome (XY) and females have two X chromosomes (XX). Males inherit the X chromosome from their mothers and the Y chromosome from their fathers. Females inherit one X chromosome from each parent.
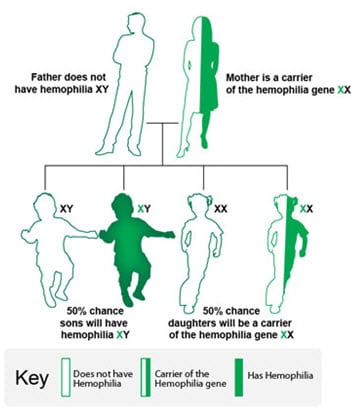 The X chromosome contains many genes that are not present on the Y chromosome. This means that males only have one copy of most of the genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have 2 copies. Thus, males can have a disease like hemophilia if they inherit an affected X chromosome that has a mutation in either the factor VIII or factor IX gene. Females can also have hemophilia, but this is much rarer. In such cases, both X chromosomes are affected, or one is affected, and the other is missing or inactive. In these females, bleeding symptoms may be similar to males with hemophilia.
The X chromosome contains many genes that are not present on the Y chromosome. This means that males only have one copy of most of the genes on the X chromosome, whereas females have 2 copies. Thus, males can have a disease like hemophilia if they inherit an affected X chromosome that has a mutation in either the factor VIII or factor IX gene. Females can also have hemophilia, but this is much rarer. In such cases, both X chromosomes are affected, or one is affected, and the other is missing or inactive. In these females, bleeding symptoms may be similar to males with hemophilia.
A female with one affected X chromosome is a “carrier” of hemophilia. Sometimes a female who is a carrier can have symptoms of hemophilia. In addition, she can pass the affected X chromosome with the clotting factor gene mutation on to her children.
Even though hemophilia runs in families, some families have no prior history of family members with hemophilia. Sometimes, there are carrier females in the family, but no affected boys, just by chance. However, about one-third of the time, the baby with hemophilia is the first one in the family to be affected with a mutation in the gene for the clotting factor.
Hemophilia can result in:
- Bleeding within joints that can lead to chronic joint disease and pain
- Bleeding in the head and sometimes in the brain which can cause long-term problems, such as seizures and paralysis
- Death can occur if the bleeding cannot be stopped or if it occurs in a vital organ such as the brain.
“Do the 5”
Key prevention messages from the National Hemophilia Foundation’s National Prevention Program
 Tips for Healthy Living
Tips for Healthy Living
- Get an annual comprehensive checkup at a hemophilia treatment center.
- Get vaccinated—Hepatitis A and B are preventable.
- Treat bleeds early and adequately.
- Exercise and maintain a healthy weight to protect your joints.
- Get tested regularly for blood-borne infections.
Types
There are several different types of hemophilia. The following two are the most common:
- Hemophilia A (Classic Hemophilia)
This type is caused by a lack or decrease of clotting factor VIII. - Hemophilia B (Christmas Disease)
This type is caused by a lack or decrease of clotting factor IX.
Signs and Symptoms
Common signs of hemophilia include:
- Bleeding into the joints. This can cause swelling and pain or tightness in the joints; it often affects the knees, elbows, and ankles.
- Bleeding into the skin (which is bruising) or muscle and soft tissue causing a build-up of blood in the area (called a hematoma).
- Bleeding of the mouth and gums, and bleeding that is hard to stop after losing a tooth.
- Bleeding after circumcision (surgery performed on male babies to remove the hood of skin, called the foreskin, covering the head of the penis).
- Bleeding after having shots, such as vaccinations.
- Bleeding in the head of an infant after a difficult delivery.
- Blood in the urine or stool.
- Frequent and hard-to-stop nosebleeds.
Who is Affected
Hemophilia occurs in about 1 of every 5,000 male births. Currently, about 20,000 males in the United States are living with the disorder. Hemophilia A is about four times as common as hemophilia B, and about half of those affected have the severe form. Hemophilia affects people from all racial and ethnic groups.
Diagnosis
Many people who have or have had family members with hemophilia will ask that their baby boys get tested soon after birth.
About one-third of babies who are diagnosed with hemophilia have a new mutation not present in other family members. In these cases, a doctor might check for hemophilia if a newborn is showing certain signs of hemophilia.
To make a diagnosis, doctors would perform certain blood tests to show if the blood is clotting properly. If it does not, then they would do clotting factor tests, also called factor assays, to diagnose the cause of the bleeding disorder. These blood tests would show the type of hemophilia and the severity.
Treatment
The best way to treat hemophilia is to replace the missing blood clotting factor so that the blood can clot properly. This is done by infusing (administering through a vein) commercially prepared factor concentrates. People with hemophilia can learn how to perform these infusions themselves so that they can stop bleeding episodes and, by performing the infusions on a regular basis (called prophylaxis), can even prevent most bleeding episodes.
Good quality medical care from doctors and nurses who know a lot about the disorder can help prevent some serious problems. Often the best choice for care is to visit a comprehensive Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC). An HTC not only provides care to address all issues related to the disorder but also provides health education that helps people with hemophilia stay healthy.
Clotting Factor Inhibitors4
About 15-20 percent of people with hemophilia develop an antibody (called an inhibitor) that stops the clotting factors from being able to clot the blood and stop bleeding. Treatment of bleeding episodes becomes extremely difficult, and the cost of care for a person with an inhibitor can skyrocket because more clotting factor or a different type of clotting factor is needed. People with inhibitors often experience more joint disease and other problems from bleeding that result in a reduced quality of life.
Treatment
Treating people who have an inhibitor is complex, and it remains one of the biggest challenges in the care of people with bleeding disorders. Some inhibitors, called “transient” inhibitors, may disappear on their own, without treatment. If possible, a person with an inhibitor should be cared for at an HTC. HTCs are specialized healthcare centers that bring together a team of doctors, nurses, and other health professionals experienced in treating people with bleeding disorders.
Some treatments for people with inhibitors include the following:
- High-Dose Clotting Factor Concentrates: People with low titer inhibitors may be treated with higher amounts or increased frequency of factor to overcome the inhibitor and yet have enough left over to form a clot.

- Bypassing Agents: Special blood products, called bypassing agents, are used to treat bleeding episodes for people with high titer inhibitors. Instead of replacing the missing factor, they go around (or bypass) the factors that are blocked by the inhibitor to help the body form a normal clot. People are taking bypassing agents should be monitored closely to make sure that their blood is not clotting too much or clotting in the wrong places in the body.
- Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) Therapy: The goal of ITI therapy is to stop the inhibitor from the blocking factor in the blood and to teach the body to accept factor as a normal part of blood. With ITI therapy, people receive large amounts of factor every day for many weeks or months.
All inhibitor treatment options require specialized medical expertise. Treatment can be costly, particularly bypass agents and ITI. People who are being treated for inhibitors should have their blood often tested to measure their inhibitor titers to be sure that treatment is working. HTCs can serve a vital role in supporting patients who undergo an intensive treatment regimen for inhibitors, such as ITI.
Get Your Son Tested Early5
In the United States, most people with hemophilia are diagnosed at a very young age. Based on CDC data, the median age at diagnosis is 36 months for people with mild hemophilia, 8 months for those with moderate hemophilia, and 1 month for those with severe hemophilia.
Jay Harold hopes you enjoyed this post, “8 Signs and Symptoms of Hemophilia: Healthy Living Tips.” Please Share it and read more about Jay Harold here. Please take this advice from Muhammad Ali and give back to others. “Service to others is the rent you pay for your room here on earth.”