Obesity is a common, serious, and costly chronic disease1. Having obesity puts people at risk for many other serious chronic diseases and increases the risk of severe illness from COVID-19. Everyone has a role to play in turning the tide against obesity and its disproportionate impact on racial and ethnic minority groups. This post ”Obesity, Race/Ethnicity, and COVID-19” seeks to provide current and relevant information from a trusted source.
{subscribe]
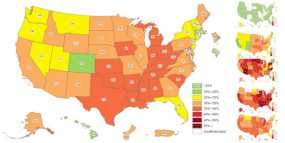
Adult Obesity is Increasing
The 2019 CDC Adult Obesity Prevalence Maps show that obesity remains high – twelve states now have an adult obesity prevalence at or above 35 percent: Alabama, Arkansas, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Tennessee, and West Virginia. This is up from nine states in 2018.
Obesity Worsens Outcomes from COVID-19
Adults with excess weight are at even greater risk during the COVID-19 pandemic:
- Having obesity increases the risk of severe illness from COVID-19. People who are overweight may also be at increased risk.
- Having obesity may triple the risk of hospitalization due to a COVID-19 infection.
- Obesity is linked to impaired immune function.
- Obesity decreases lung capacity and reserve and can make ventilation more difficult.
- As BMI increases, the risk of death from COVID-19 increases.
- Studies have demonstrated that obesity may be linked to lower vaccine responses for numerous diseases (influenza, Hepatitis B, tetanus).
Overweight, Obesity and Severe Obesity
Having obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) between 30 kg/m2 and <40 kg/m2 or severe obesity (BMI of 40 kg/m2 or above), increases your risk of severe illness from COVID-192. Having overweight, defined as a BMI > 25 kg/m2 but less than 30 kg/m2 might increase your risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Actions to take
- Take your prescription medicines for overweight, obesity, or severe obesity exactly as prescribed.
- Make sure that you have at least a 30-day supply of your medicines.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for nutrition and physical activity, while maintaining social distancing precautions.
- Call your healthcare provider if you have concerns or feel sick.
- If you don’t have a healthcare provider, contact your nearest community health center or health department.
Obesity Disproportionately Impacts Some Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups

Combined data from 2017-2019 show notable racial and ethnic disparities:
- Non-Hispanic Black adults had the highest prevalence of self-reported obesity (39.8%), followed by Hispanic adults (33.8%), and non-Hispanic White adults (29.9%).
- 6 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic White adults.
- 15 states had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among Hispanic adults.
- 34 states and the District of Columbia (D.C.) had an obesity prevalence of 35 percent or higher among non-Hispanic Black adults.
Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black adults have a higher prevalence of obesity and are more likely to suffer worse outcomes from COVID-19. Racial and ethnic minority groups have historically not had broad opportunities for economic, physical, and emotional health, and these inequities have increased the risk of getting sick and dying from COVID-19 for some groups. Many of these same factors are contributing to the higher level of obesity in some racial and ethnic minority groups.
What Can be Done
Obesity is a complex disease with many contributing factors. Neighborhood design, access to healthy, affordable foods and beverages, and access to safe and convenient places for physical activity can all impact obesity. The racial and ethnic disparities in obesity underscore the need to address social determinants of health such as poverty, education, and housing to remove barriers to health. This will take action at the policy and systems-level to ensure that obesity prevention and management starts early, and that everyone has access to good nutrition and safe places to be physically active. Policymakers and community leaders must work to ensure that their communities, environments, and systems support a healthy, active lifestyle for all.
Steps to Take Now
Systemic change takes time, as does long-term weight loss. In addition to the steps everyone should take to slow the spread of COVID-19, individuals can help protect themselves and their families during this pandemic by:

Eating a healthy diet
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains as well as the appropriate amount of calories is important for your health, and can help with weight loss and preventing weight gain. Good nutrition can help support optimal immune function. A healthy diet can help prevent or support self-management of diseases such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes , which also increases the risk of severe illness from COVID-19.
Being active
Regular physical activity helps you feel better, sleep better, and reduce anxiety. It can also help with preventing weight gain and when combined with calorie reduction, helps with weight loss. Physical activity can also help prevent diseases that increase a person’s chances of having severe illness from COVID-19 such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Emerging research suggests it may also help boost immune function.
Getting enough sleep
Insufficient sleep has been linked to depression, as well as chronic diseases that may increase the risk of severe illness from COVID-19 such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.

Coping with stress
Stress during an infectious disease outbreak can sometimes cause changes in sleep or eating patterns, increased use of alcohol and tobacco, or worsening of chronic health problems.
Over time, these actions can help individuals with obesity improve their overall health. And if they result in even modest weight loss, there are health benefits, such as improvements in blood pressure, blood cholesterol, and blood sugars. And with a lower BMI, the risk of severe illness from COVID-19 is reduced.
What CDC, Partners, States, and Communities are Doing
Our work with partners, states, and communities makes it easier for everyone to move more and eat a healthy diet where they live, learn, work, and play. Together, we work to remove barriers and promote health and wellness for all by:

- Bringing communities together to plan and carry out local, culturally tailored interventions to address poor nutrition, and physical inactivity, and tobacco use
- Promoting healthier food and beverage choices in childcare, schools, workplaces, hospitals, and public venues
- Making healthy foods more available by connecting local producers with retailers and organizations such as childcare, schools, hospitals, and food hubs
- Promoting nutrition standards in early care and education settings, food pantries, and faith-based organizations
- Designing communities that connect sidewalks, bicycle routes, and public transportation with homes, early care and education settings, schools, parks, and workplaces
- Ensuring screening for obesity and access to healthy lifestyle programs for children and their families
The epidemic of obesity is impacting the severity of the COVID-19 pandemic. Given the added risks associated with COVID-19, we need to support all individuals, especially members of racial and ethnic minority groups, to live active healthy lives.
Jay Harold hopes you enjoyed this post, “Obesity, Race/Ethnicity, and COVID-19.” Please share it and read more about Jay Harold here. Please take this advice from Muhammad Ali and give it back to others. “Service to others is the rent you pay for your room here on earth.”