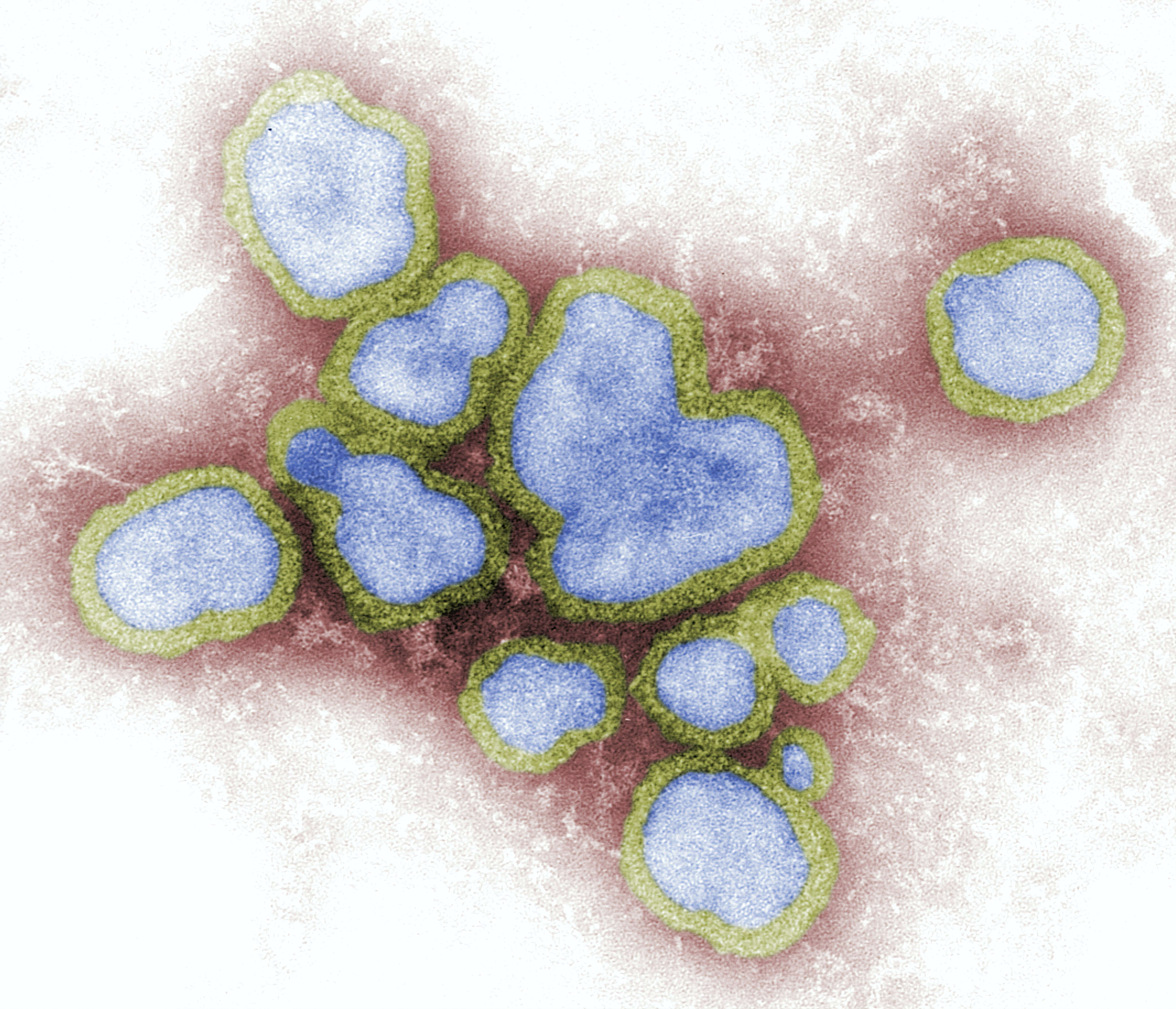
Influenza (Flu) and COVID-19 are both contagious respiratory illnesses, but they are caused by different viruses1. COVID-19 is caused by infection with a new coronavirus (called SARS-CoV-2) and flu is caused by infection with influenza viruses. This post ”What’s the difference between Flu and COVID-19?” seeks to provide current and relevant information from a trusted source.
There are some key differences between flu and COVID-19. COVID-19 seems to spread more easily than flu and causes more serious illnesses in some people. It can also take longer before people show symptoms and people can be contagious for longer. Another important difference is there is a vaccine to protect against flu. There is currently no vaccine to prevent COVID-19. The best way to prevent infection is to avoid being exposed to the virus. More information about the differences between flu and COVID-19 is available in the different sections below.
Because some of the symptoms of flu and COVID-19 are similar, it may be hard to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone, and testing may be needed to help confirm a diagnosis. Flu and COVID-19 share many characteristics, but there are some key differences between the two.
While more is learned every day, there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and the virus that causes it. This page compares COVID-19 and flu, given the best available information to date.
Does a flu vaccine increase your risk of getting COVID-19?
There is no evidence that getting a flu vaccine increases your risk of getting sick from a coronavirus, like the one that causes COVID-19.
You may have heard about a study published in January 2020 that reported an association between flu vaccination and the risk of four commonly circulating seasonal coronaviruses, but not the one that causes COVID-19. This report was later found to be incorrect.
The results from that initial study led researchers in Canada to look at their data to see if they could find similar results in their population. The results from Canada’s study showed that flu vaccination did not increase the risk for these seasonal coronaviruses. The Canadian findings highlighted the protective benefits of flu vaccination.
The Canadian researchers also identified a flaw in the methods of the first study, noting that it violated the part of the study design that compares vaccination rates among patients with and without flu. This flaw led to the incorrect association between flu vaccination and seasonal coronavirus risk. When these researchers reexamined data from the first study using correct methods, they found that flu vaccination did not increase the risk for infection with other respiratory viruses, including seasonal coronaviruses.
What is the difference between Influenza (Flu) and COVID-192?
Influenza (Flu) and COVID-19 are both contagious respiratory illnesses, but they are caused by different viruses. COVID-19 is caused by infection with a new coronavirus (called SARS-CoV-2) and flu is caused by infection with influenza viruses.
There are some key differences between flu and COVID-19. COVID-19 seems to spread more easily than flu and causes more serious illnesses in some people. It can also take longer before people show symptoms and people can be contagious for longer. Another important difference is there is a vaccine to protect against flu. There is currently no vaccine to prevent COVID-19. The best way to prevent infection is to avoid being exposed to the virus. More information about the differences between flu and COVID-19 is available in the different sections below.
Because some of the symptoms of flu and COVID-19 are similar, it may be hard to tell the difference between them based on symptoms alone, and testing may be needed to help confirm a diagnosis. Flu and COVID-19 share many characteristics, but there are some key differences between the two.
While more is learned every day, there is still a lot that is unknown about COVID-19 and the virus that causes it. This page compares COVID-19 and flu, given the best available information to date.
Similarities:
Both COVID-19 and flu can have varying degrees of signs and symptoms, ranging from no symptoms (asymptomatic) to severe symptoms. Common symptoms that COVID-19 and flu share include:
- Fever or feeling feverish/chills
- Cough
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Fatigue (tiredness)
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose

- Muscle pain or body aches
- Headache
- Some people may have vomiting and diarrhea, though this is more common in children than adults
Differences:
Flu
Flu viruses can cause mild to severe illness, including common signs and symptoms listed above.
COVID-19
COVID-19 seems to cause more serious illnesses in some people. Other signs and symptoms of COVID-19, different from flu, may include a change in or loss of taste or smell.
How long symptoms appear after exposure and infection
Similarities:
For both COVID-19 and flu, 1 or more days can pass between a person becoming infected and when he or she starts to experience illness symptoms.
Differences:
If a person has COVID-19, it could take them longer to develop symptoms than if they had flu.
Flu
Typically, a person develops symptoms anywhere from 1 to 4 days after infection.
 COVID-19
COVID-19
Typically, a person develops symptoms 5 days after being infected, but symptoms can appear as early as 2 days after infection or as late as 14 days after infection, and the time range can vary.
How long someone can spread the virus
Similarities:
For both COVID-19 and flu, it’s possible to spread the virus for at least 1 day before experiencing any symptoms.
Differences:
If a person has COVID-19, they may be contagious for a longer period of time than if they had flu.
Flu
Most people with flu are contagious for about 1 day before they show symptoms.
Older children and adults with flu appear to be most contagious during the initial 3-4 days of their illness but many remain contagious for about 7 days.
Infants and people with weakened immune systems can be contagious for even longer.
COVID-19
How long someone can spread the virus that causes COVID-19 is still under investigation.
It’s possible for people to spread the virus for about 2 days before experiencing signs or symptoms and remain contagious for at least 10 days after signs or symptoms first appeared. If someone is asymptomatic or their symptoms go away, it’s possible to remain contagious for at least 10 days after testing positive for COVID-19.
Know how it spreads2
- COVID-19 spreads easily from person to person, mainly by the following routes:
- Between people who are in close contact with one another (within 6 feet).
- Through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes breathe, sings, or talks.
- Respiratory droplets cause infection when they are inhaled or deposited on mucous membranes, such as those that line the inside of the nose and mouth.
- People who are infected but do not have symptoms can also spread the virus to others.
Less common ways COVID-19 can spread
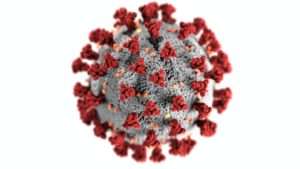
- Under certain circumstances (for example, when people are in enclosed spaces with poor ventilation), COVID-19 can sometimes be spread by airborne transmission.
- COVID-19 spreads less commonly through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Everyone Should
Wash your hands often
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds especially after you have been in a public place, or after blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing.
- It’s especially important to wash:
- Before eating or preparing food
- Before touching your face
- After using the restroom
- After leaving a public place
- At the end of blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing
- After handling your mask
- After changing a diaper
- Following caring for someone sick
- After touching animals or pets
- If soap and water are not readily available, use a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol. Cover all surfaces of your hands and rub them together until they feel dry.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth with unwashed hands.

Avoid close contact
- Inside your home: Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- If possible, maintain 6 feet between the person who is sick and other household members.
- Outside your home: Put 6 feet of distance between yourself and people who don’t live in your household.
- Remember that some people without symptoms may be able to spread the virus.
- Stay at least 6 feet (about 2 arms’ length) from other people.
- Keeping distance from others is especially important for people who are at higher risk of getting very sick.
Cover your mouth and nose with a mask when around others
- You could spread COVID-19 to others even if you do not feel sick.
- The mask is meant to protect other people in case you are infected.
- Everyone should wear a mask in public settings and when around people who don’t live in your household, especially when other social distancing measures are difficult to maintain.
- Masks should not be placed on young children under age 2, anyone who has trouble breathing, or is unconscious, incapacitated, or otherwise unable to remove the mask without assistance.
- Do NOT use a mask meant for a healthcare worker. Currently, surgical masks and N95 respirators are critical supplies that should be reserved for healthcare workers and other first responders.
- Continue to keep about 6 feet between yourself and others. The mask is not a substitute for social distancing.
Cover coughs and sneezes
- Always cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze or use the inside of your elbow and do not spit.
- Throw used tissues in the trash.
- Immediately wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap and water are not readily available, clean your hands with a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol.
Clean and disinfect
- Clean AND disinfect frequently touched surfaces daily. This includes tables, doorknobs, light switches, countertops, handles, desks, phones, keyboards, toilets, faucets, and sinks.
- If surfaces are dirty, clean them. Use detergent or soap and water before disinfection.
- Then, use a household disinfectant. Most common EPA-registered household disinfectants will work.
Monitor Your Health Daily
- Be alert for symptoms. Watch for fever, cough, shortness of breath, or other symptoms of COVID-19.

- Especially important if you are running essential errands, going into the office or workplace, and in settings where it may be difficult to keep a physical distance of 6 feet.
- Take your temperature if symptoms develop.
- Don’t take your temperature within 30 minutes of exercising or after taking medications that could lower your temperature, like acetaminophen.
- Follow CDC guidance if symptoms develop.
Protect Your Health This Flu Season
Flu viruses and the virus that causes COVID-19 will likely both spread this fall and winter. Healthcare systems could be overwhelmed treating both patients with flu and patients with COVID-19. This means getting a flu vaccine during 2020-2021 is more important than ever.
While getting a flu vaccine will not protect against COVID-19 there are many important benefits, such as:
- Flu vaccines have been shown to reduce the risk of flu illness, hospitalization, and death.
- Getting a flu vaccine can also save healthcare resources for the care of patients with COVID-19.
How do flu vaccines work3?
The seasonal flu vaccine protects against the influenza viruses that research indicates will be most common during the upcoming season. Most flu vaccines in the United States protect against four different flu viruses (“quadrivalent”); an influenza A (H1N1) virus, an influenza A (H3N2) virus, and two influenza B viruses. Some flu vaccines protect against three different flu viruses (“trivalent”); an influenza A (H1N1) virus, an influenza A (H3N2) virus, and one influenza B virus. Two of the trivalent vaccines are designed specifically for people 65 and older to create a stronger immune response.Flu vaccines cause antibodies to develop in the body about two weeks after vaccination. These antibodies provide protection against infection with the viruses that are used to make the vaccine.
What kinds of flu vaccines are available?
CDC recommends the use of any licensed, age-appropriate influenza vaccine during the 2020-2021 influenza season, including inactivated influenza vaccine [IIV], recombinant influenza vaccine [RIV], or live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV). No preference is expressed for any influenza vaccine over another. Both trivalent (three-ingredient) and quadrivalent (four-ingredient) influenza vaccines will be available.

Trivalent flu vaccines include:
A trivalent flu shot made using an adjuvant (an ingredient that helps create a stronger immune response), approved for people 65 years of age and older.
Quadrivalent flu vaccines include:
Standard-dose quadrivalent influenza shots that are manufactured using virus grown in eggs. These include Afluria Quadrivalent, Fluarix Quadrivalent, FluLaval Quadrivalent, and Fluzone Quadrivalent. Different influenza shots are licensed for different age groups. These four vaccines are approved for people 6 months of age and older. Most influenza shots are given in an arm muscle with a needle. One quadrivalent influenza shot (Afluria Quadrivalent) can be given either with a needle (for people aged 6 months and older) or with a jet injector (for people aged 18 through 64 years only).
5 Types of Flu Shots
A quadrivalent cell-based influenza shot (Flucelvax Quadrivalent) containing virus grown in cell culture, which is licensed for people 4 years and older. This vaccine is egg-free.
Recombinant quadrivalent influenza shot (Flublok Quadrivalent), an egg-free vaccine, is approved for people 18 years and older.
A quadrivalent flu shot using an adjuvant (an ingredient that helps create a stronger immune response), approved for people 65 years of age and older.
The quadrivalent high-dose influenza vaccine (Fluzone High-Dose), licensed for people 65 years and older.
There are many flu vaccine options to choose from, but the most important thing is for all people 6 months and older to get a flu vaccine every year. If you have questions about which vaccine is best for you, talk to your doctor or other health care professional. More information on approved flu vaccines for the 2020-2021 flu season, and age indications for each vaccine are available in CDC’s Table: U.S. Influenza Vaccine Products for the 2020-2021 Season
Are any of the available flu vaccines recommended over others?
For the 2020-2021 flu season, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends annual influenza (flu) vaccination for everyone 6 months and older with any licensed, influenza vaccine that is appropriate for the recipient’s age and health status, including inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV), recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV), or live attenuated nasal spray influenza vaccine (LAIV4) with no preference expressed for any one vaccine over another.
There are many vaccine options to choose from, but the most important thing is for all people 6 months and older to get a flu vaccine every year. If you have questions about which vaccine is best for you, talk to your doctor or other health care professional
Bibliography
- https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm#:~:text=Influenza%20(Flu)%20and%20COVID%2D19%20are%20both%20contagious%20respiratory,by%20infection%20with%20influenza%20viruses.
- https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/flu/prevent/keyfacts.htm